
What is Blockchain
Blockchain is perhaps one of the biggest technology innovations of the past decade. Everyone has been talking about it—but beneath the headlines there’s not always a clear understanding of what blockchain is or how it works. Despite its impervious reputation, the basic idea behind blockchain is actually pretty simple. And it has great potential to change industries from the bottom up.
Blockchain technology allows multiple parties to share and maintain a digital ledger of transactions in a secure and transparent way. This of a chain of blocks, each of which contains a list of transactions. These blocks are linked together in a chronological order, creating a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain.
Blockchain is a secure and permanent record of data ownership stored in blocks within a list, and it can be accessed by multiple parties. There are different types of blockchains, such as public, private, and consortium blockchains. Blockchain development is disrupting the financial industry by providing more efficient and cost-effective services. Blockchain can be used as an alternative to traditional financial systems due to its transparency, reliability, and audibility. Blockchain development services can help build decentralized applications or private blockchains, as well as develop smart contracts on platforms like Ethereum or Hyperledger Fabric.
No alterations can be made to a transaction which has been saved in the blockchain; it is immutable. This is what makes this technology so unique for recording and tracking financial transactions, and any data in general.
Blockchains use cryptography to secure and validate transactions, and they can be either public or private. Unlike private blockchains, which are typically restricted for utilization within a certain organization or consortium, anyone can take part in the network and validate transactions on blockchain networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are both publicly accessible.
The decentralized structure of a blockchain network allows multiple parties to have a copy of the ledger and ensures that no single party has control over the data. This makes it a secure and transparent way to record and track transactions, while also reducing the need for intermediaries.
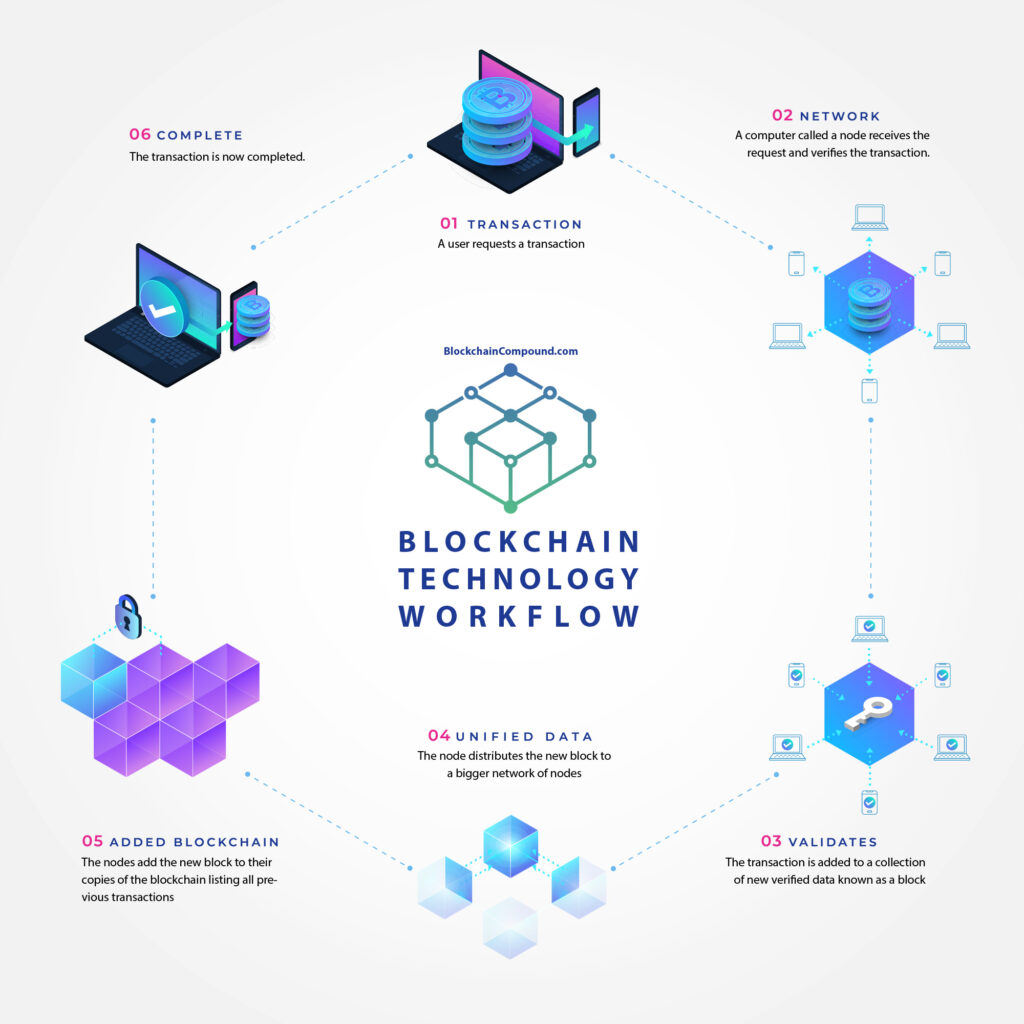
History of Blockchain, Where did it come from?
So where did this technology come from? It’s origin is to this day an intriguing mystery. In 2008 the famous Bitcoin whitepaper was published by an unknown individual or some thing a group of individuals using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. In 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto revolutionized digital payments when they logged onto a decentralized network of computers and sent 10 bitcoins to Hal Finney. This transaction marked Bitcoin’s entrance into mainstream culture and outlined a new electronic cash system with no need for intermediaries. Since then, blockchain technology has expanded far beyond digital currency in its use cases and applications.
Industries like finance, supply chain, healthcare, and even the government, are all exploring the use of blockchain technology because of its benefits. For example It helps them increase transparency, reduce costs, and improve security.
It’s worth noting that the concept of blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT) existed before the creation of Bitcoin. When it comes to digital currency, Bitcoin was and remains the pioneer of decentralization based on blockchain. It is the first instance of a successful implementation of such a system.
Decentralization
A unique feature of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. It refers to the distribution of decision-making power and control across multiple participants in a network, rather than being concentrated in a single central authority or point of control like a Bank.
Rather than having the data stored and recorded at a single, central location, decentralized networks store the information across a range of computers.
This means that there is no single point of failure, making these systems more secure and robust.
It also implies that no individual has full control over the network – therefore increasing transparency and accountability.
These advantages are useful for various activities such as banking, finance and supply chain management – allowing people to securely exchange data and value without needing any intermediaries.
Gain further insight into decentralization’s merits with this article.
Protocol
Ensuring that data is transmitted and handled correctly between different devices and systems requires the implementation of protocols, which provide an organized structure for communication. In computer networking, protocols define the format and order of messages exchanged between devices, as well as the procedures for handling errors, detecting duplicates, and ensuring reliable delivery. The use of protocols is key to blockchain technology, as they determine the rules and operations of the system. Through protocol, transactions can be verified and processed securely, with no single point of failure. This decentralization eliminates a centralized control, making it more transparent and accountable, which makes it useful for diverse applications like finance, banking and supply chain management. To learn further about these advantages of decentralization this article offers insight into the subject matter. Protocols an important component for many systems and technologies, because they ensure compatibility and interoperability between different parts of the system.
Immutable Ledger
First off let’s start with the definition of immutable.
The term "immutable" means that something is unchangeable, permanent, or cannot be altered. It implies that once something is created or recorded, it remains in its original form and cannot be modified or tampered with. In the context of computer science and technology, "immutable" is often used to describe data structures, such as blockchain ledgers, that are designed to be resistant to modification or deletion.
So, an immutable ledger refers to a tamper-proof and permanent record of transactions stored on a blockchain network. The term “immutable” means unalterable, and the ledger is designed so that once a transaction is recorded and confirmed, it cannot be altered, deleted, or tampered with. This characteristic of immutability provides a high degree of security and trust, as all parties on the network can rely on the accuracy and consistency of the ledger over time.
Unlike a centralized system, where a single authority or intermediary controls and manages the ledger, a decentralized network relies on many nodes to keep its ledger maintained and updated. This not only increases the security of data stored within it, but also makes it more transparent to all parties involved. Furthermore, everyone is able to access this information simultaneously.
The immutability of a blockchain ledger is due to its decentralized nature. Rather than being controlled by a single entity, a blockchain is maintained by a network of computers that work together to validate and add new blocks to the chain. Once a block has been added to the chain, it becomes a permanent part of the record and cannot be altered without the consensus of the network.
This feature of immutability has a range of applications in many industries, including finance, supply chain management, and voting systems. In finance, the immutability of blockchain ledgers can improve transparency and reduce the risk of fraud. For example, a bank can use blockchain to record transactions between different banks, providing a secure and transparent record of all transactions.
In supply chain management, blockchain can be used to create a transparent record of the movement of goods from the manufacturer to the consumer. This can help to prevent fraud, reduce waste and increase efficiency in the supply chain.
In voting systems, the immutability of blockchain can be used to ensure that each vote is counted accurately and that the results are tamper-proof. This is particularly important in elections where there is a risk of interference or tampering with the results.
However, while the immutability of blockchain provides many benefits, it can also present challenges. For example, if incorrect data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be removed or changed. This means that the integrity of the entire blockchain can be compromised if there is a mistake or a deliberate attempt to manipulate the data.
To mitigate this risk, many blockchain implementations include mechanisms to ensure data accuracy and protect against fraudulent activity. These may include consensus mechanisms, such as proof of work or proof of stake, which require network participants to solve complex cryptographic puzzles or stake cryptocurrency to validate transactions and blocks.
Distributed Ledger
A distributed ledger is a database that is spread across a network of computers, rather than being centralized in one location. Each participant in the network has a copy of the ledger, and all copies are updated in real-time as transactions are recorded.
Distributed ledgers existed before the emergence of Bitcoin, and were used in various contexts, such as financial systems, supply chain management, and voting systems. However, the technology became widely known and popularized through the use of blockchain, which is a specific type of distributed ledger.
A blockchain is a type of distributed ledger that consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. Each block in the chain is linked to the previous one through cryptographic hashes, which creates an immutable and tamper-proof record of all transactions that have occurred on the network.
One of the main benefits of a distributed ledger, and particularly a blockchain, is that it eliminates the need for a trusted third-party intermediary to verify and record transactions. Instead, the network participants collectively maintain and validate the ledger through a consensus mechanism, which is a set of rules for agreeing on the state of the ledger.
In a blockchain, the consensus mechanism typically involves a process called mining, where network participants compete to solve a complex mathematical puzzle, and the first participant to solve the puzzle earns the right to add a block to the chain and receive a reward in the form of cryptocurrency.
Distributed ledgers have a number of potential benefits, such as increased transparency, security, and efficiency in transaction processing. For example, a distributed ledger could be used to create a transparent and secure record of a supply chain, allowing consumers to track the origin and authenticity of products.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to the technology, such as scalability limitations, regulatory challenges, and concerns about energy consumption in blockchain networks that rely on mining.
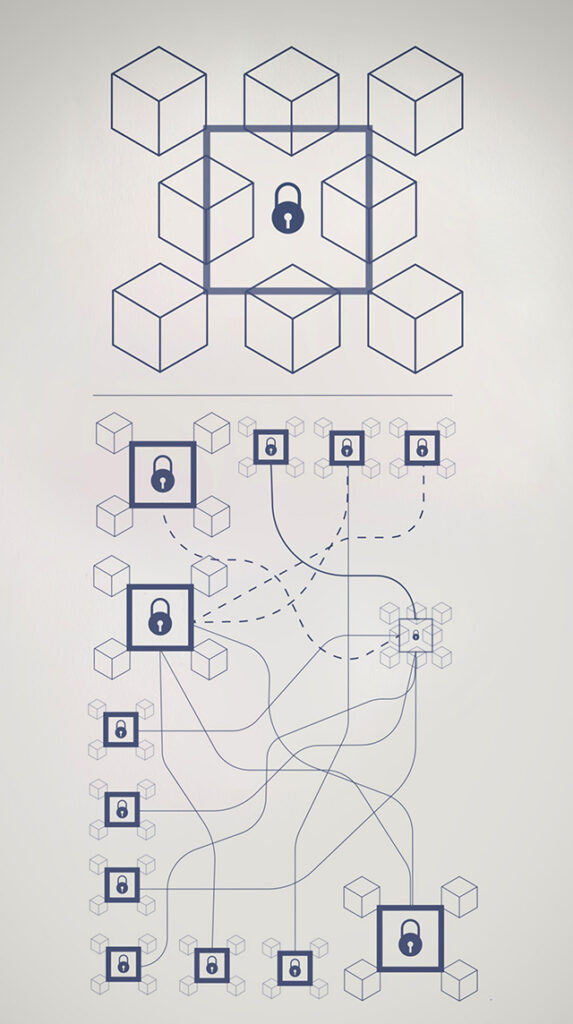
Why is it important that blockchain have a distributed ledger?
It is important for a blockchain to have a distributed ledger because it provides several key benefits that make it a powerful tool for secure and transparent record-keeping. A distributed ledger is a network of computers that work together to maintain a single, synchronized copy of the blockchain. This means that the ledger is not controlled by a single entity or central authority, but rather is shared and maintained by all network participants.
One of the key benefits of a distributed ledger is that it provides a high degree of security and resilience. Because the ledger is distributed across many computers, it is highly resistant to attacks or attempts to tamper with the data. In order for an attacker to successfully alter the blockchain, they would need to compromise a majority of the network’s computing power, which is very difficult and resource-intensive.
Another benefit of a distributed ledger is that it provides a high degree of transparency and accountability. Because all network participants have access to the same copy of the ledger, it is easy to verify the authenticity of transactions and ensure that they have not been tampered with. This can be particularly useful in industries where transparency is important, such as supply chain management, where the movement of goods can be tracked and verified on the blockchain.
Finally, a distributed ledger can help to reduce the risk of fraud or errors in record-keeping. Because all network participants have access to the same copy of the ledger, it is easy to detect and correct any errors or discrepancies. This can help to improve the accuracy and reliability of record-keeping and reduce the risk of fraud or other types of financial crime.
Consensus Algorithm
A consensus algorithm is a mechanism used by a blockchain network to reach a shared agreement on the state of the network and validate transactions. The purpose of the consensus algorithm is to prevent double-spending, ensure security, and prevent malicious actors from compromising the integrity of the network.
There are several popular consensus algorithms used by blockchain networks, including:
- Proof of Work (PoW): This is the first consensus algorithm that was introduced with Bitcoin. It requires participants to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): This is a more energy-efficient alternative to PoW. In PoS, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and lock in the network.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): In this algorithm, token holders can vote for delegates who will validate transactions and create new blocks.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): This is a consensus algorithm used by permissioned blockchains, where all participants are known. It ensures that the network can continue to function even if some participants behave maliciously.
The choice of consensus algorithm is crucial for the security, scalability, and efficiency of a blockchain network. Different consensus algorithms are suitable for different types of use cases, and the choice of algorithm should be made based on the specific requirements of the network.
Is Blockchain secure?
Blockchain technology is considered to be secure, since it uses cryptography to secure and validate transactions. The decentralized structure of a blockchain network ensures that no single party has control over the data. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it can’t be changed, creating a permanent record of the transaction.
However, it’s important to note that the security of a blockchain system depends on how it is implemented and configured. A poorly implemented or configured blockchain system can be vulnerable to attacks. For example, a vulnerability in the smart contract code can be exploited by hackers to steal funds.
Also, it is possible for a 51% attack to happen on a blockchain network, where a group of miners or validators control more than 50% of the network’s computing power. This type of attack can allow them to manipulate the ledger, double-spend coins, or block other miners from adding new blocks to the chain.
Additionally, it’s also important to keep in mind that the security of a blockchain system is also dependent on the security of the devices and infrastructure that run it, as well as the security practices of its users.
In summary, Blockchain technology is considered to be secure, but the security of a blockchain system can be affected by the implementation, configuration, the number of participants, and the security practices of its users.
Doesn’t the FTX collapse prove that blockchain is a scam?
The recent collapse of the FTX exchange does not prove that blockchain technology is a scam. Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It allows for secure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries.
The collapse of FTX is not a failure of blockchain technology, but rather a failure of the exchange itself. Like any other technology, the implementation and execution of blockchain can be flawed, leading to security breaches or other issues. However, this does not mean that the underlying technology is inherently flawed or a scam. It is important to carefully evaluate and research the security measures in place for any platform or exchange before using it.
How is the blockchain being used today?
Blockchain technology can be used in a wide range of industries and applications, in fact it is already being used in several ways today like in these examples below:
- Financial Services: Blockchain technology is being used in the financial sector to increase transparency, reduce costs, and improve security in areas such as cross-border payments, supply chain finance, and digital identity.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology can be used to create tamper-proof, transparent and secure supply chain management systems. It can be used to track the movement of goods, from point A to the point B (origin to consumption).
- Digital Identity: Blockchain technology can be used to create digital identities that are secure, private, and portable, and can be used for voting systems, access control, and more.
- Healthcare: Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent electronic health records (EHRs), which can be shared between patients and healthcare providers.
- Real estate: Blockchain technology can be used to track the ownership of properties and facilitate transactions, making the process more efficient and transparent.
- Gaming: Blockchain technology is being used to create decentralized, digital assets that can be bought, sold, and traded, like in-game items, and also to create decentralized gaming platforms.
- Energy: Think of decentralized energy systems, which would allow for peer-to-peer energy trading, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing transparency.
- Charity: Blockchain technology can be used to create transparency in charity organizations and to track the funds and how they are used.
There are many other areas of research and development that are ongoing in the field. Blockchain technology will continue to evolve and new use cases will emerge.
How are blockchain, , decentralized finance, and cryptocurrency connected?
Blockchain, cryptocurrency, and decentralized finance (DeFi) are interconnected concepts in the digital finance world.
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. It enables secure and transparent record-keeping and is used as the underlying technology for many cryptocurrencies.
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security and operates independently of a central bank. Bitcoin was the first. By now almost everyone has at least heard of it.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) refers to financial applications and services built on blockchain technology that allow for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. DeFi enables a more accessible, transparent, and secure financial system that operates without central authority.
In DeFi, blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies play a crucial role. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs), stablecoins, yield farming, and lending and borrowing platforms are some of the popular DeFi applications that use blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies.
In short, blockchain provides the infrastructure for secure and transparent transactions, cryptocurrency acts as a medium of exchange, and DeFi leverages both to create new financial applications and services in a decentralized and trustless environment
Explain blockchain to a child
"The Adventures of Little Bit: A Story About Blockchain"Once upon a time, in the land of computers and technology, there was a special kind of technology called blockchain. Little Bit was a young and curious blockchain who loved to explore and learn new things.
One day, Little Bit heard about a magical place called the internet, where all kinds of information and money could be exchanged. Little Bit wanted to visit this place, so he set off on an adventure.
As Little Bit traveled, he met many different types of technologies, but none of them were quite as special as blockchain. Blockchain technology was like a digital ledger that recorded all the transactions that happened on the internet. It was very secure and couldn’t be changed or cheated.
Little Bit was fascinated and wanted to learn more about how blockchain worked. He met other blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Bitcoin was the first and it was used to send and receive money without the need for a bank. Ethereum was a little bit different, it allowed people to create special computer programs called smart contracts that could automatically complete tasks.
As Little Bit’s adventure continued, he saw how blockchain was being used in many different ways, such as in supply chain management, digital identity, and voting systems.
Little Bit realized that blockchain technology was going to be very important in the future and he wanted to be a part of it. So he decided to stay and continue to learn and grow with blockchain technology.
The Current Top 3 Blockchains
The three top blockchain platforms as of 2023
Currently, the three most widely used blockchain platforms are:
Bitcoin: Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency. It was created in 2009 and has since become the largest and most valuable blockchain network in the world. Bitcoin uses a proof-of-work consensus mechanism and is primarily used for digital currency transactions.
Ethereum: Ethereum is a decentralized platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It was launched in 2015 and has since become the second largest blockchain network. Ethereum uses a proof-of-work consensus mechanism and it aims to be a blockchain platform for building decentralized applications.
Binance Smart Chain: Binance Smart Chain is a blockchain platform developed by Binance, one of the largest cryptocurrency exchanges. It was launched in 2020 and aims to provide high-performance smart contracts for decentralized applications. Binance Smart Chain is a smart contract platform that is built on a modified version of Tendermint consensus.
These three blockchains are the most widely used, but there are many other blockchain platforms in use today, each with its own set of features and capabilities. Some other notable blockchain platforms include: Ripple, TRON, EOS, Litecoin, Cardano, IOTA, Cosmos, Solana, and many more.
How does it work? Does it need Internet? Does it need Power?
The blockchain does not rely on the internet to function. The blockchain is a decentralized network that operates independently from the internet. The internet is used as a means to access and interact with the blockchain, but a crash of the internet would not necessarily result in a crash of the blockchain. The blockchain has its own infrastructure and mechanisms, such as consensus algorithms, to ensure its continued operation and data integrity, even in the absence of the internet.
With that said though, blockchain technology does not work without power. The nodes in the network require electricity to operate, store, and transmit data. If there is a power outage, the network would be temporarily disabled, and any transactions or updates would not be processed until power is restored. This is why it is so important for blockchain networks to have robust backup power systems in place in order to be able to continue to function in the event of a power failure.
The network continues to operate
A blockchain network, like any other computer-based system, requires power to operate. However, the key aspect of decentralization is that no single entity controls or operates the network, but rather it is maintained by a network of nodes spread across the world. The nodes work together to validate and record transactions, and in the event of a power outage in one location, the network can continue to operate as long as there are enough nodes still functioning. This helps to ensure that the network is not vulnerable to single points of failure and can continue to operate even if some nodes are temporarily unable to participate. In this way, a blockchain network is designed to be decentralized and resilient to power outages and other disruptions, even if it does require some amount of power to function.
How might blockchain look in the future?
Keep in mind that Blockchain technology is still in its early stages of development, and it is expected to evolve significantly over the next few years. With that said below are some of the ways in which blockchain technology may evolve in the future:
Scalability: Scalability remains a significant challenge for many blockchain networks, especially public ones like Bitcoin and Ethereum. As more people adopt blockchain and more applications are built on top of it, the need for scalability solutions that can handle high volumes of transactions will become more pressing.
Interoperability: Different blockchain networks currently operate in silos and don’t easily interact with each other. This can create friction for users who need to move assets from one network to another. The development of interoperability solutions that enable seamless cross-chain transactions is expected to be a key area of growth in the blockchain space.
Privacy: While blockchain technology provides transparency and immutability, it is not naturally designed to provide privacy. As privacy concerns become more pressing, the development of privacy-focused blockchain solutions is expected to increase.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written directly into code. They have the potential to automate many business processes and reduce the need for intermediaries. As the use of smart contracts becomes more widespread, their functionality is likely to evolve and become more sophisticated.
Regulation: As blockchain technology continues to gain adoption, governments and regulators are likely to become more involved in setting standards and regulations for the industry. This may impact the way in which blockchain technology is developed and used in the future.
Decentralized finance (DeFi): Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a growing area of innovation in the blockchain space, and its development is expected to continue. DeFi applications and services, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), yield farming, and lending and borrowing platforms, are likely to become more sophisticated and offer new financial instruments and opportunities to users.
Overall, the evolution of blockchain technology will be shaped by a combination of technological advancements, user needs, and regulatory developments.
VIDEO - How Blockchain Works in 6 Minutes
The YouTube channel Simply Explain has a nice video it did explaining how blockchain works.




